Web Services Architecture
Web Services are an Internet protocol-based interface to processing. As one would expect, Web Services are generally stateless and follow a request/response model of interaction. Web Services standards provide a way to locate interfaces and exchange data in an understandable way. For Intranet applications, SOAP messages may be received directly by application servers. For extranet applications, because of security concerns, SOAP messages are likely to be received by Web Servers or integration servers that pass the messages on to the appropriate applications.
Other than the interface to the service, there are no requirements as to how the services are provided. For instance, a Web Services front end can be added to an existing information-processing infrastructure. This is particularly useful for organizations that have an existing infrastructure in place. Figure 2.1 shows an example of how Web Services can be provided in this way. Alternately, applications can be engineered to use a consistent Web Services model in all tiers.
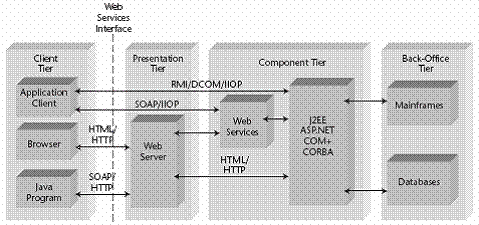
Figure 2.1 Typical Web Services environment
Next >> Web Services Security |